High blood pressure is a global cause of heart attacks, kidney failures, cardiovascular diseases, and strokes. A reduction in blood pressure has essential health benefits both for individuals and for populations.
Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a better eating plan, stopping smoking, and increasing physical activity, can aid in reducing blood pressure.
Diet and lifestyle have a significant influence on the development of hypertension. It is a modifiable factor that can be improved to lower blood pressure.
Research shows that plant-based diets lower blood pressure by providing the human body with large amounts of fiber, minerals, and vitamins.
Plant-based diets are rich in calcium, magnesium, potassium, and unsaturated fatty acids, which positively impact high blood pressure.
Keep reading to explore more about it!
Understanding Blood Pressure and its Risks
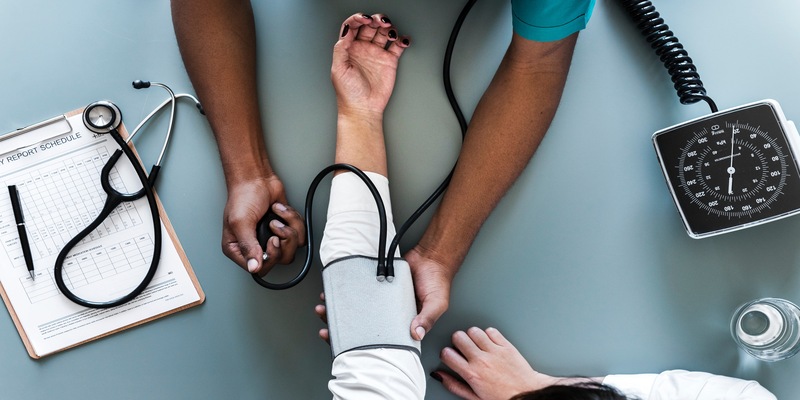
High blood pressure occurs when blood pressure against the walls of your arteries remains too high consistently. This can harm your arteries over time, potentially causing severe problems such as heart attack and stroke.
Often, there are no noticeable symptoms, leading individuals with high blood pressure to believe they are healthy. However, it can cause permanent harm or even be fatal if not treated.
Frequent checks of your blood pressure can help both you and your physician in noticing any alterations. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a better eating plan and increasing physical activity, can aid in reducing blood pressure.
Moreover, consuming a diet rich in plants enhances the well-being of your digestive system, enabling your body to more effectively utilize the nutrients from food that boost your immune function and lower your blood pressure.
Overview of Plant Based Diets
A plant-based diet encompasses fruits and vegetables, nuts, seeds, oils, whole grains, legumes, and beans. Fruits and vegetables are rich in vital nutrients unavailable from other food sources. These nutrients, phytochemicals, and antioxidants in plants play a crucial role in maintaining the health of your cells and keeping your body in harmony, thereby enhancing your immune system's performance.
Not only this, these nutrients are also effective in combating inflammation within the body. Similarly, the small phytochemicals and antioxidants that strengthen your immune system also circulate throughout your body, neutralizing harmful substances such as environmental pollutants, processed foods, bacteria, and more.
How a Plant Based Diet Affects Blood Pressure?

Multiple research studies indicate that individuals adhering to vegetarian diets tend to have lower blood pressure levels than those who consume meat.
Specific research suggests that a diet rich in potassium, characteristic of a plant-based diet, can reduce high blood pressure. Potassium-rich foods include fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
Additionally, Potassium acts in a way that counteracts sodium's effects, decreasing blood pressure. Magnesium and Calcium also play a beneficial role in managing high blood pressure.
These nutrients are abundant in green leafy vegetables like spinach and legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
A vegetarian diet offers polyunsaturated fatty acids, which, when consumed in large amounts, may positively reduce hypertension.
The extent to which these protective effects are influenced by increased vasomotor activity and blood pressure regulation remains uncertain and calls for further investigation.
How to Get Started With a Plant Based Diet?

- Choose vegetables over meat. Have smaller amounts of meat and plenty of colorful vegetables on your plate. Use your meat as a garnish instead of a main course.
- Your snack time may include some vegetables and salsa or hummus as a dressing.
- Choose nuts, avocados, seeds, olive oil, and butter as a source of fats, as these are comparatively healthy options.
- Salad greens are a cherry on top. You are on the right track if your dinner includes a bowl of green vegetables such as spinach, fresh herbs, beans, romaine, or red leafy green.
- A peach, watermelon slice, or juicy apple can quickly satisfy your dessert cravings for a sweet bite after having your food.
- Whole grains, vegetables, and beans should be added to your meals at least twice weekly.
Cost and Market Trends for Plant Based Foods
The growing trend of this generation opting for meat-free or plant-based diets shows a significant shift in dietary habits from earlier generations.
Everyone, from working officials to athletes, supports the new wave of eating plant-based foods. Many big companies and corporate sectors are investing high-profile funding in food value chains worldwide.
Like most diets, your food cost will depend on your meal plans, the ingredients, and the food brands you choose.
According to an online survey, vegetarians and vegans spend $1 less per meal than those who eat meat. That averages $23 per week, $99 monthly, or $1,196 yearly.
The growth of plant-based foods shows a significant consumer interest that matches their beliefs, fulfilling their desires for sustainability and fairness.
It highlights the adaptability of plant-based food businesses that overcame supply issues and demonstrated steadfast dedication to developing creative, tasty meals for every event.
Summary
Research Shows That Plant-Based Diets Lower Blood Pressure by providing fiber, minerals, and vitamins such as Calcium, Magnesium, Potassium, and unsaturated fatty acids.
Multiple studies indicate that individuals adhering to vegetarian diets tend to have comparatively lower blood pressure levels than those who consume meat.
Frequent blood pressure checks can help detect alterations, and a plant-rich diet enhances well-being. All in all, plant-based eating plans vary greatly, and picking the one that suits your needs the most is essential.







